Network Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP) is a revolutionary technology in the world of modern surveying and geolocation. Developed by the Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services (RTCM), NTRIP serves as a standardized protocol designed to facilitate the transfer of GNSS corrections data over the Internet.
For those working in precision agriculture, construction, land surveying, and autonomous vehicle navigation, this advanced system plays a critical role in providing real-time, high-accuracy location data that supports the utmost efficiency and accuracy.
What is NTRIP?
NTRIP is an online protocol for streaming Differential GNSS (DGNSS) or Real-Time Kinematic correction data. It enables the delivery of RTK correction data from the base station to the rover (mobile receiver).
Essentially, NTRIP is the “streaming service” that packages and delivers the corrections data. NTRIP can stream Differential GPS (DGPS) and Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) correction data in order to provide high precision location information.
How does NTRIP work?
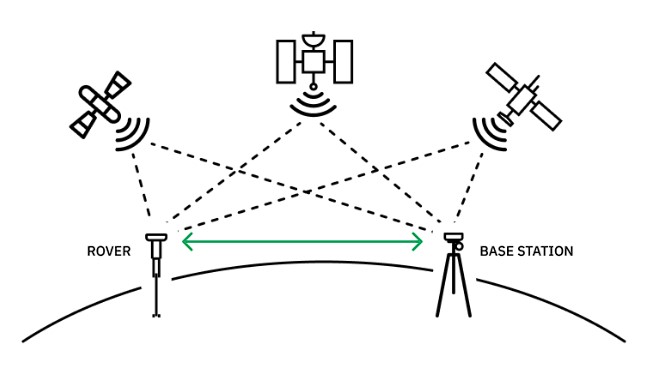
NTRIP operates as a sophisticated system designed to transmit GNSS correction data from a stationary reference station to a mobile GNSS receiver, known as a rover, via the internet. In other words, it provides the pathway for signals to travel between a base station and a receiver.
- Data Collection and Processing: The process begins with data collection at the base stations, which are strategically positioned and have known coordinates. These stations receive signals from GNSS satellites. The base stations collect raw satellite data and transmit their precise location and satellite measurements to the NTIRIP cast, our station is right here in Coleman Ab.
- NTRIP Transmission: NTRIP is then used to transmit the correction data required by RTK systems. The NTRIP caster acts as an intermediary, streaming the raw GNSS data from the base stations over the internet to the receiver. This protocol ensures efficient and reliable delivery of the data.
- GNSS Receivers Receive Data and Perform Corrections: Once the data is transmitted through NTRIP, GNSS receivers, also known as rovers, complete a mathematical calculation by comparing the measurements from the satellites with the precise location data from the base stations, resulting in high-accuracy positioning to the centimeter level.
By leveraging the power of the internet, NTRIP offers a reliable and efficient method for delivering GNSS correction data to rovers with no need for a second local receiver to act as a base. For businesses looking to integrate the highest level of precision in their location-based services, selecting the best NTRIP service provider is crucial.
By partnering with an NTRIP service provider you’re not just acquiring data; you’re enabling precision, efficiency, and innovation in your operations.
How do RTK corrections work?

Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) corrections provide a sophisticated enhancement to various GNSS satellite data, including GPS. These systems provide location data with reasonable accuracy, but factors such as atmospheric disturbances, satellite orbital variance, multipath effects, and clock inaccuracies can introduce errors. As a result, the location data is accurate within meters.
RTK corrections are designed to mitigate these inaccuracies and provide centimeter-level accuracy by supplying additional data points. RTK corrections rely on a network of base stations that cover a large geographic area. These stations receive GNSS signals and calculate errors in the data based on their known precise locations. Altogether, this creates an RTK network.
Each station acts as a fixed base, continuously monitoring GNSS signals. Once the station determines the necessary corrections by noting discrepancies between the GNSS data and their known location, that information is sent via NTRIP to the RTK receivers. By leveraging the speed of the internet, NTRIP ensures that the correction data is delivered efficiently and in real time to users.
